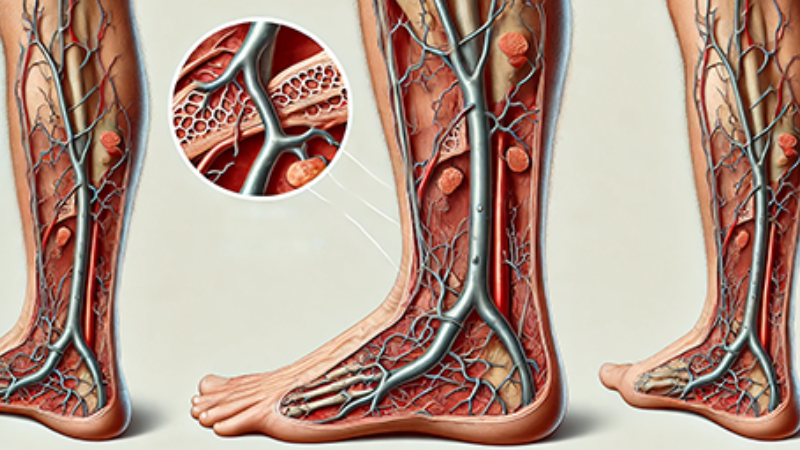
What is Venous Insufficiency?
Venous insufficiency is a condition where blood cannot adequately return to the heart from the veins in the legs. This problem typically arises due to the weakening or damage of the vein valves. The valves are small structures that ensure blood flows in one direction and prevent backflow. When the valves do not function properly, blood can pool in the legs, leading to venous insufficiency. Symptoms often include swelling, pain, and fatigue in the legs, and if left untreated, it can result in serious health complications.
What Causes Venous Insufficiency?
The primary causes of venous insufficiency include genetic predisposition, aging, obesity, prolonged standing or sitting, and inactivity. Genetic factors can increase the risk of developing the condition in individuals with a family history of venous insufficiency. With aging, the vein valves may weaken, leading to venous insufficiency. Obesity exerts extra pressure on the veins in the legs, making it difficult for blood to flow. Prolonged standing or sitting can impede blood from returning to the heart. Additionally, inactivity can negatively affect blood circulation, contributing to venous insufficiency.
What Types of Venous Insufficiency Are There?
Venous insufficiency is generally categorized into two main types: superficial venous insufficiency and deep venous insufficiency. Superficial venous insufficiency affects the veins close to the skin's surface and is often associated with varicose veins. In this case, the veins enlarge and become twisted. Deep venous insufficiency affects the veins located deeper within the muscles and is usually a more serious condition. Deep venous insufficiency can cause more intense swelling and pain in the legs. Both types can lead to complications if left untreated and can decrease quality of life.
What Are the Symptoms of Chronic Venous Insufficiency?
The symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency typically develop gradually and worsen over time. The most common symptoms include swelling in the legs, especially increasing pain and a feeling of heaviness as the day progresses. Changes in skin color, particularly brown spots around the ankles, eczema, and ulcers are also among the symptoms. Itching, cramping, and a feeling of restlessness in the legs are common signs as well. If untreated, chronic venous insufficiency can lead to serious skin infections and ulcers.
How is Venous Insufficiency Treated?
Treatment for venous insufficiency varies depending on the severity of the condition and the symptoms present. In the initial stage, lifestyle changes and simple measures are often recommended. Patients can engage in regular exercise, elevate their legs, lose weight, and avoid prolonged standing or sitting. Compression stockings can be used to improve blood flow in the legs. In more serious cases, medical treatment options such as sclerotherapy, laser treatment, or surgical intervention may be applied. Sclerotherapy is a treatment where a solution is injected to damage the inner walls of the veins. Laser treatment uses laser energy to close off the vein. Surgical intervention involves removing or tying off damaged veins.
Frequently Asked Questions About Venous Insufficiency
Is venous insufficiency hereditary?
Yes, venous insufficiency can be related to genetic factors. Individuals with a family history of venous insufficiency are at higher risk of developing the condition.
What happens if venous insufficiency is left untreated?
If left untreated, venous insufficiency can lead to serious complications, including skin infections, ulcers, and deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Does exercise prevent venous insufficiency?
Regular exercise strengthens the leg muscles and improves blood circulation, which can reduce the risk of venous insufficiency.
What exercises are beneficial for venous insufficiency?
Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, and cycling can improve blood flow in the legs and provide protection against venous insufficiency.
Can venous insufficiency be completely treated?
Venous insufficiency cannot be completely cured, but symptoms can be managed and complications prevented. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help prevent the progression of the disease.
When should I see a doctor?
If you experience persistent swelling, pain, skin changes, or ulcers in your legs, it is important to consult a doctor. These symptoms may indicate venous insufficiency or other serious health issues.


